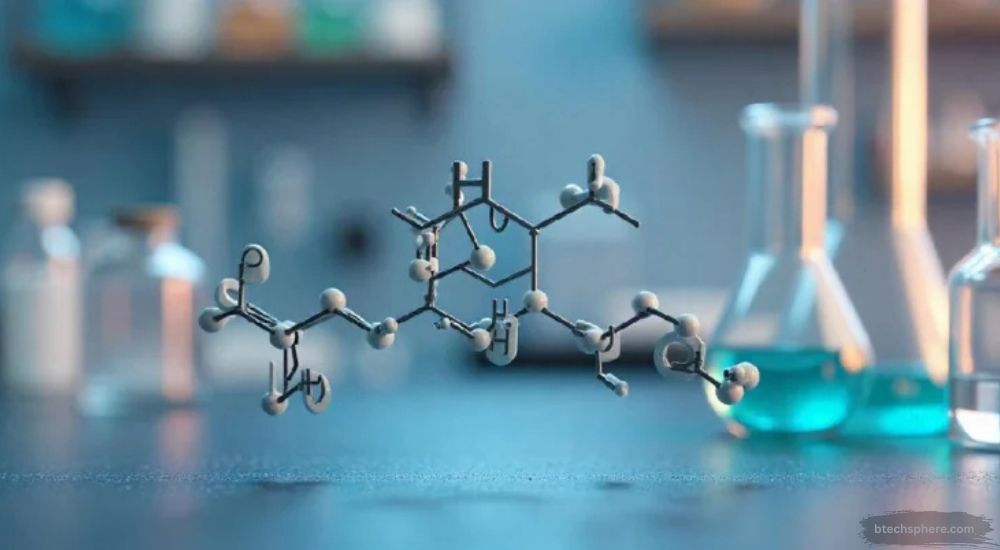
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a fascinating compound that captures attention due to its structural complexity and diverse industrial significance. It is related to the class of organic compounds that combine formate and other carbon-based groups, creating a bridge between simple organic acids and more reactive intermediates. This compound can exhibit unique behaviors when mixed with water, often resulting in changes in molecular stability, polarity, and reactivity that are important in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Chemical Formula Explained
The chemical notation HCOOCH CH2 H2O suggests a combination of formate (HCOO) and an organic group (CH2) interacting with water (H2O). Each part of the formula carries specific functional properties. The HCOO portion refers to formic acid derivatives, known for their reactivity and role as intermediates in esterification and oxidation processes. The CH2 group represents a basic hydrocarbon unit, while H2O symbolizes the aqueous or hydration component that influences solubility and molecular interaction.
Molecular Composition and Structure
From a structural perspective, HCOOCH CH2 H2O displays the relationship between carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a balanced but reactive arrangement. The carbon atoms form the backbone of the molecule, while the oxygen atoms introduce polarity through their electronegativity, making the compound both versatile and reactive. The presence of water can contribute to hydrogen bonding, enhancing the molecule’s ability to dissolve and participate in chemical reactions efficiently.
Physical Properties of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
HCOOCH CH2 H2O exhibits several unique physical characteristics that define its stability and usability in various chemical applications. It typically appears as a transparent or slightly viscous liquid, depending on its purity and temperature conditions. The compound dissolves well in water, showing high polarity due to the presence of oxygen atoms that encourage hydrogen bonding.
Key Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Clear to slightly viscous liquid.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and polar solvents.
- Boiling Point: Moderate, varying with concentration and pressure.
- Odor: Mild, similar to that of light esters or alcohols.
- Density: Medium range, influenced by moisture and temperature.
- Volatility: Moderate, allowing partial evaporation under open-air conditions.
These physical traits make HCOOCH CH2 H2O versatile in laboratory and industrial processes where solubility, stability, and controlled reactivity are crucial for synthesis and analysis.
Chemical Properties and Behavior
Chemically, HCOOCH CH2 H2O behaves as a reactive intermediate that can undergo hydrolysis, oxidation, or condensation under controlled conditions. The formate group makes it prone to mild oxidation reactions, while the CH2 unit can serve as an attachment point for other organic modifications. The presence of water can act as both a stabilizer and a reactant, depending on the temperature and environmental conditions during reactions.
Synthesis of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
The preparation of HCOOCH CH2 H2O often involves esterification reactions between formic acid derivatives and alcohols under the influence of catalysts. Water either emerges as a by-product or is incorporated intentionally to modify reaction kinetics. Laboratory synthesis typically employs controlled heating and monitoring to achieve desired concentrations and purity levels, emphasizing the balance between organic reactivity and aqueous stability.
Reactions Involving HCOOCH CH2 H2O
In reaction mechanisms, this compound demonstrates its versatility. It can act as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate depending on the context. For example, it may decompose into simpler molecules like carbon dioxide and methanol under certain conditions or react with oxidizing agents to form aldehydes and carboxylic acids. Such reactivity makes it valuable for studying kinetic behaviors and chemical transformations in organic chemistry.
Role of Water (H2O) in the Compound
Water (H2O) plays a vital role in defining the chemical behavior and stability of HCOOCH CH2 H2O. It acts as a medium that supports hydrogen bonding and enhances the solubility of the compound. The polar nature of water allows it to interact with other components, influencing both the reaction speed and molecular balance.
Key Points:
- Water increases the solubility of the compound in polar environments.
- It stabilizes reactive molecules through hydrogen bonding.
- Acts as a catalyst or reactant in certain chemical reactions.
- Helps control the compound’s temperature and reaction kinetics.
- Maintains equilibrium between the organic and aqueous phases during reactions.
Applications in Chemical Industries
HCOOCH CH2 H2O has found uses in various industrial processes, particularly in organic synthesis, solvent formulation, and catalyst development. It can act as a mild reagent for esterification and polymerization reactions. Moreover, its solubility and reactivity make it suitable for use in coatings, adhesives, and as a component in specialized chemical blends. Its adaptability ensures it remains relevant across multiple chemical engineering applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety Measures
Like many organic compounds, HCOOCH CH2 H2O requires careful handling to prevent environmental contamination or safety hazards. While not highly toxic, prolonged exposure can cause irritation or respiratory discomfort. Industrial protocols emphasize proper ventilation, controlled disposal, and the use of protective equipment during handling. Environmentally, its decomposition products—primarily carbon dioxide and water—are relatively benign, but uncontrolled release into water systems should still be avoided.
Importance in Organic Chemistry
In the field of organic chemistry, HCOOCH CH2 H2O holds educational and experimental importance. It serves as a representative example of formate-based compounds that illustrate the relationship between structure and reactivity. Students and researchers use it to explore reaction mechanisms involving esters, alcohols, and carboxylic acids. It provides a foundation for understanding how small changes in molecular structure can dramatically affect chemical behavior.
Biochemical Relevance and Interactions
Though primarily synthetic, compounds similar to HCOOCH CH2 H2O have biochemical analogs that participate in metabolic pathways. Formate derivatives play roles in enzymatic reactions within living organisms, influencing cellular energy processes. While this exact molecule may not occur naturally, its chemistry mirrors biological transformations that convert carbon-based molecules into usable energy or structural components.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper storage conditions are essential to maintain the stability of HCOOCH CH2 H2O. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers away from direct sunlight and high temperatures. Because it may absorb moisture or react with strong oxidizers, it’s best stored in a cool, dry environment. Laboratories and industries adhere to safety data sheets (SDS) for guidance on handling, spill control, and emergency procedures.
Experimental Uses in Laboratories
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is often explored in laboratories to understand its reactivity, solubility, and structural behavior under different experimental conditions. Its chemical balance between formate and hydrocarbon groups makes it ideal for research focused on organic reaction mechanisms and chemical synthesis.
Points:
- It is commonly used as a model compound in studying esterification and hydrolysis reactions.
- Researchers use it to analyze solvent effects on molecular stability and polarity.
- It plays a role in developing reaction kinetics models for organic and aqueous environments.
- In controlled studies, it helps chemists observe the influence of temperature and catalysts on reaction rates.
- It serves as a reagent in producing secondary compounds, particularly in experimental organic synthesis.
Future Potential and Research Scope
With the growing demand for efficient, sustainable, and environmentally safe chemicals, HCOOCH CH2 H2O and its derivatives are gaining attention. Researchers are exploring its potential in green chemistry, focusing on its ability to serve as a mild, biodegradable reagent. Continued innovation in this field may uncover new industrial and pharmaceutical applications that rely on its adaptable chemical properties.
Conclusion
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is more than just a chemical formula—it’s a bridge between theoretical chemistry and practical application. Its structure, reactivity, and versatility make it a subject of ongoing study and industrial use. Understanding this compound not only enhances our grasp of organic chemistry but also opens pathways to safer, more sustainable chemical innovations.