In the intricate structure of our respiratory system, some areas remain quietly unnoticed until they cause discomfort. One such hidden yet vital structure is the adenoid. When the adenoids become swollen or inflamed, the condition is known as adenoidid. While the term may sound medical and distant, its effects are surprisingly close to home, influencing breathing, sleep quality, and overall comfort. This condition is especially common in children but can also occur in adults. By taking a gentle, informed approach, we can understand what adenoidid is, why it happens, and how it can be managed with care.
Understanding the Role of the Adenoids
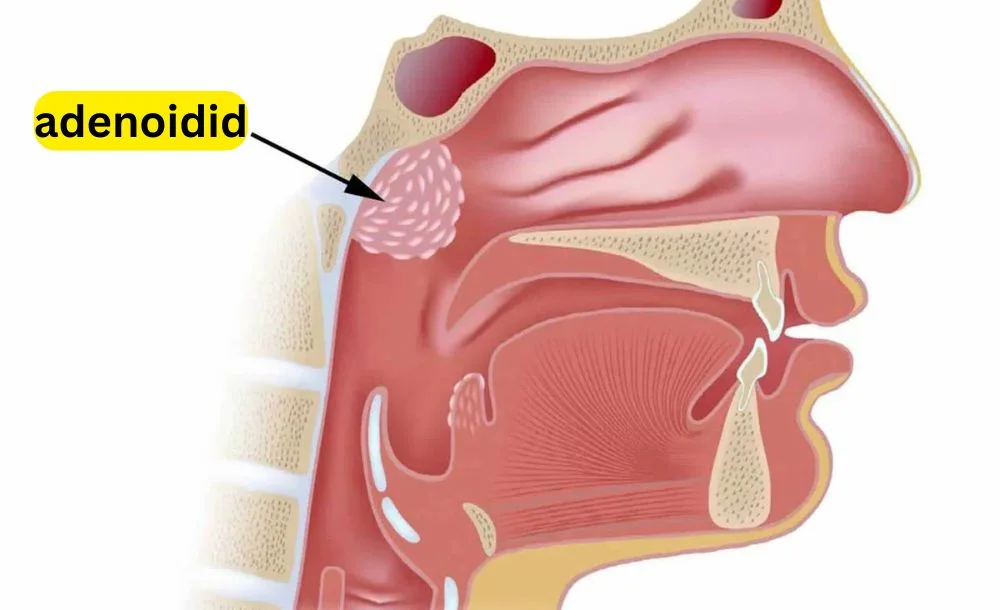
Adenoids are small masses of lymphatic tissue situated high in the throat, behind the nose. Because of their hidden position, they cannot be seen simply by looking into the mouth. Their primary function is to act as a protective filter for the body’s immune system, especially during early childhood. Adenoids trap harmful bacteria and viruses entering through the nose or mouth, helping to prevent infections from spreading deeper into the body.
During childhood, the adenoids are relatively large and active, providing an important layer of defense while the immune system is still developing. As we grow older, their role gradually becomes less essential. By adulthood, adenoids often shrink in size or even disappear entirely. Despite this natural change, their importance during childhood cannot be understated and when they become inflamed, it can significantly affect daily comfort and health.
Causes behind Adenoidid
Adenoidid occurs when the adenoids become swollen due to irritation or infection. The reasons for this inflammation can vary widely, ranging from common illnesses to environmental triggers.Viral infections are among the most common causes, with colds, influenza, and other respiratory illnesses often leading to temporary swelling. Bacterial infections, such as strep throat, can also result in inflammation, sometimes requiring antibiotics for proper treatment.
Allergies are another frequent cause, particularly seasonal allergies triggered by pollen, dust mites, mold spores, or pet dander. In these cases, the adenoids respond to allergens in much the same way they do to germs by swelling to block potential threats. Environmental factors also play a role. Children and adults exposed to polluted air, cigarette smoke, or very dry indoor environments may experience irritation of the adenoid tissue, increasing the likelihood of adenoidid.For some children, repeated infections can lead to chronic or recurrent adenoidid, where swelling becomes a regular occurrence rather than an occasional problem.
Recognizing the Signs with Care
Identifying adenoidid is not always straightforward because of the adenoids’ hidden location. However, the symptoms often present themselves in noticeable ways if we pay close attention. A blocked or stuffy nose that persists beyond the duration of a normal cold is a common sign. Mouth breathing, particularly at night, is another clue, as swollen adenoids can obstruct airflow through the nasal passages. This can lead to snoring, restless sleep, and frequent waking during the night.
Children with adenoidid might develop a nasal-sounding voice, and some may experience a constant sore throat or post-nasal drip. Ear infections can also be a symptom, as swollen adenoids may block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup and discomfort. In severe or prolonged cases, repeated swelling can affect facial development in children, underscoring the importance of timely care.
Diagnosis of Adenoidid
When adenoidid is suspected, an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist will conduct an evaluation. This typically begins with a discussion of symptoms and medical history. The doctor may use a small, flexible endoscope to view the adenoids directly, or they might recommend an X-ray to determine their size and position.These diagnostic methods are generally quick and cause minimal discomfort. Their purpose is to confirm the presence of inflammation and guide decisions about the most suitable treatment options.
Treatment Approaches for Adenoidid
Treatment for adenoidid depends on its cause, severity, and frequency of occurrence. In mild cases, the body often heals naturally with the right support. Rest, adequate hydration, and a balanced diet are key components of recovery.Warm drinks, gentle soups, and steam inhalation can ease throat irritation and help clear congestion. Nasal saline sprays may also be recommended to keep the nasal passages moist and reduce swelling. When a bacterial infection is confirmed, antibiotics may be prescribed.
If allergies are contributing to the inflammation, managing these triggers is essential. This may involve antihistamines, nasal sprays, or adjustments in the home environment to minimize exposure to allergens.In more severe or chronic cases, where adenoidid causes persistent breathing problems or repeated ear infections, an adenoidectomy may be advised. This minor surgical procedure removes the adenoids entirely. It is most often performed in children and typically results in quick recovery and long-term relief from symptoms.
The Link between Adenoidid and Ear Health
The adenoids are located close to the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the nose. When adenoidid causes swelling in this area, it can block these tubes, preventing fluid from draining properly. This can lead to recurrent ear infections, fluid buildup, and even temporary hearing loss.
This link is particularly important in children, as frequent ear infections can affect hearing during critical stages of speech and language development. Addressing adenoidid promptly can help prevent these complications and support healthy growth.
Supporting Recovery at Home
Whether treated medically or surgically, recovery from adenoidid can be supported through small but effective measures at home. Maintaining clean indoor air is one of the most important steps, which may include regular dusting, vacuuming, and the use of air purifiers.A humidifier can help keep the air moist, especially in dry climates or during the winter months when indoor heating can reduce humidity levels. Offering warm herbal teas or broths can soothe throat irritation, while ensuring plenty of rest allows the body to focus on healing.
Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke and strong odors is equally important, as these can irritate the respiratory system and prolong recovery. Encouraging gentle outdoor activity in fresh air, when appropriate, can also help improve breathing and overall well-being.
Preventing Future Episodes of Adenoidid
Prevention focuses on supporting the immune system and reducing exposure to known triggers. Regular handwashing is a simple but effective way to prevent infections that could lead to adenoidid. Managing allergies through prescribed medication or lifestyle changes can also make a significant difference.
Good indoor air quality is another important factor. This can be achieved by ensuring proper ventilation, using air filters, and keeping the home environment free from dust and allergens. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps strengthen the immune system, reducing the risk of frequent infections.Although it is not always possible to prevent adenoidid entirely, these steps can reduce its frequency and severity, promoting long-term respiratory health.
Living Comfortably with Healthy Adenoids
Adenoidid may be hidden from sight, but its impact is often felt in our daily comfort and health. From making breathing difficult to disrupting sleep, it can influence various aspects of well-being. Fortunately, with early recognition, proper treatment, and supportive home care, it is a condition that can be managed effectively.
For children, addressing adenoidid promptly helps ensure that it does not interfere with growth, learning, or speech development. For adults, it can restore comfort and ease in breathing, contributing to overall health.By understanding adenoidid in a calm, informed way, we not only treat the condition but also develop greater appreciation for the small yet vital parts of our body that keep us healthy. A proactive approach, supported by gentle care, ensures that our breathing remains effortless and our rest undisturbed.
FAQs About Adenoidid
Is adenoidid the same as enlarged adenoids?
Not exactly. Adenoidid refers to inflammation, while enlarged adenoids may result from repeated inflammation or other causes.
Can adenoidid go away without treatment?
Yes, mild cases can resolve naturally with rest and supportive care. However, persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a doctor.
Is surgery always needed for adenoidid?
No, surgery is recommended only in chronic or severe cases that cause significant breathing or ear problems.
How long does recovery take?
Mild cases usually improve within a week or two, while recovery from an adenoidectomy typically takes just a few days.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent adenoidid?
Yes, maintaining clean indoor air, managing allergies, and practicing good hygiene can help reduce the risk of recurrence.